3217. 从链表中移除在数组中存在的节点
题目描述
给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个链表的头节点 head。从链表中移除所有存在于 nums 中的节点后,返回修改后的链表的头节点。
示例 1:
输入: nums = [1,2,3], head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [4,5]
解释:
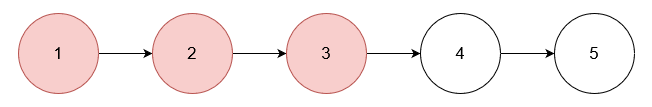
移除数值为 1, 2 和 3 的节点。
示例 2:
输入: nums = [1], head = [1,2,1,2,1,2]
输出: [2,2,2]
解释:
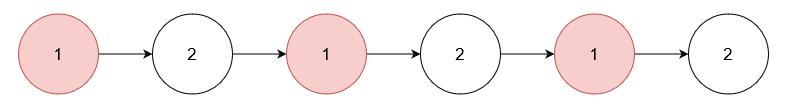
移除数值为 1 的节点。
示例 3:
输入: nums = [5], head = [1,2,3,4]
输出: [1,2,3,4]
解释:
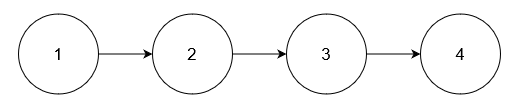
链表中不存在值为 5 的节点。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105nums中的所有元素都是唯一的。- 链表中的节点数在
[1, 105]的范围内。 1 <= Node.val <= 105- 输入保证链表中至少有一个值没有在
nums中出现过。
解法
方法一:哈希表
我们可以使用一个哈希表 $\textit{s}$ 来存储数组 $\textit{nums}$ 中的所有元素,然后定义一个虚拟节点 $\textit{dummy}$,将其指向链表的头节点 $\textit{head}$。
接下来,我们遍历从虚拟节点 $\textit{dummy}$ 开始的链表,如果当前节点的下一个节点的值在哈希表 $\textit{s}$ 中,我们就将当前节点的指针指向下下个节点,否则我们就将当前节点指针指向下一个节点。
最后,我们返回虚拟节点 $\textit{dummy}$ 的下一个节点。
时间复杂度 $O(n + m)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 为数组 $\textit{nums}$ 的长度,而 $m$ 为链表 $\textit{head}$ 的长度。
Python3
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def modifiedList(
self, nums: List[int], head: Optional[ListNode]
) -> Optional[ListNode]:
s = set(nums)
pre = dummy = ListNode(next=head)
while pre.next:
if pre.next.val in s:
pre.next = pre.next.next
else:
pre = pre.next
return dummy.next
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode modifiedList(int[] nums, ListNode head) {
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
for (int x : nums) {
s.add(x);
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (ListNode pre = dummy; pre.next != null;) {
if (s.contains(pre.next.val)) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
} else {
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* modifiedList(vector<int>& nums, ListNode* head) {
unordered_set<int> s(nums.begin(), nums.end());
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (ListNode* pre = dummy; pre->next;) {
if (s.count(pre->next->val)) {
pre->next = pre->next->next;
} else {
pre = pre->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func modifiedList(nums []int, head *ListNode) *ListNode {
s := map[int]bool{}
for _, x := range nums {
s[x] = true
}
dummy := &ListNode{Next: head}
for pre := dummy; pre.Next != nil; {
if s[pre.Next.Val] {
pre.Next = pre.Next.Next
} else {
pre = pre.Next
}
}
return dummy.Next
}
TypeScript
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function modifiedList(nums: number[], head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
const s: Set<number> = new Set(nums);
const dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
for (let pre = dummy; pre.next; ) {
if (s.has(pre.next.val)) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
} else {
pre = pre.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}