938. Range Sum of BST
Description
Given the root node of a binary search tree and two integers low and high, return the sum of values of all nodes with a value in the inclusive range [low, high].
Example 1:
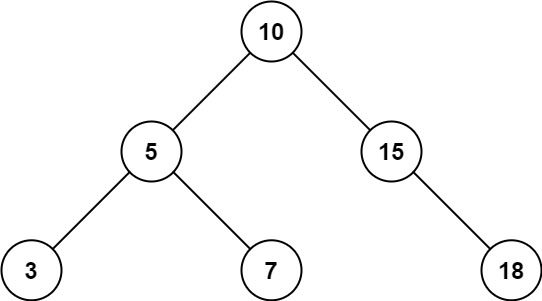
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15 Output: 32 Explanation: Nodes 7, 10, and 15 are in the range [7, 15]. 7 + 10 + 15 = 32.
Example 2:
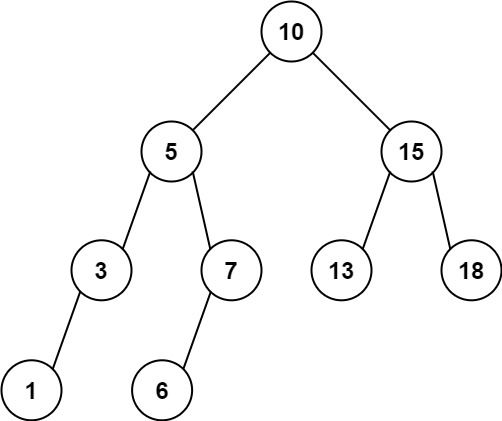
Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10 Output: 23 Explanation: Nodes 6, 7, and 10 are in the range [6, 10]. 6 + 7 + 10 = 23.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 2 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 1051 <= low <= high <= 105- All
Node.valare unique.
Solutions
Solution 1: DFS
We design a function $dfs(root)$, which represents the sum of the values of all nodes in the subtree with $root$ as the root, and the values are within the range $[low, high]$. The answer is $dfs(root)$.
The execution logic of the function $dfs(root)$ is as follows:
If $root$ is null, return $0$.
If the value $x$ of $root$ is within the range $[low, high]$, then the initial answer of the function $dfs(root)$ is $x$, otherwise it is $0$.
If $x > low$, it means that there may be nodes in the left subtree of $root$ with values within the range $[low, high]$, so we need to recursively call $dfs(root.left)$ and add the result to the answer.
If $x < high$, it means that there may be nodes in the right subtree of $root$ with values within the range $[low, high]$, so we need to recursively call $dfs(root.right)$ and add the result to the answer.
Finally, return the answer.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Where $n$ is the number of nodes in the binary search tree.
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> int:
def dfs(root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
x = root.val
ans = x if low <= x <= high else 0
if x > low:
ans += dfs(root.left)
if x < high:
ans += dfs(root.right)
return ans
return dfs(root)
Java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
return dfs(root, low, high);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int x = root.val;
int ans = low <= x && x <= high ? x : 0;
if (x > low) {
ans += dfs(root.left, low, high);
}
if (x < high) {
ans += dfs(root.right, low, high);
}
return ans;
}
}
C++
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int rangeSumBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
function<int(TreeNode*)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int x = root->val;
int ans = low <= x && x <= high ? x : 0;
if (x > low) {
ans += dfs(root->left);
}
if (x < high) {
ans += dfs(root->right);
}
return ans;
};
return dfs(root);
}
};
Go
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* type TreeNode struct {
* Val int
* Left *TreeNode
* Right *TreeNode
* }
*/
func rangeSumBST(root *TreeNode, low int, high int) int {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) int
dfs = func(root *TreeNode) (ans int) {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
x := root.Val
if low <= x && x <= high {
ans += x
}
if x > low {
ans += dfs(root.Left)
}
if x < high {
ans += dfs(root.Right)
}
return
}
return dfs(root)
}
TypeScript
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode {
* val: number
* left: TreeNode | null
* right: TreeNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
* }
*/
function rangeSumBST(root: TreeNode | null, low: number, high: number): number {
const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null): number => {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
const { val, left, right } = root;
let ans = low <= val && val <= high ? val : 0;
if (val > low) {
ans += dfs(left);
}
if (val < high) {
ans += dfs(right);
}
return ans;
};
return dfs(root);
}
C#
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public int RangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
return dfs(root, low, high);
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int x = root.val;
int ans = low <= x && x <= high ? x : 0;
if (x > low) {
ans += dfs(root.left, low, high);
}
if (x < high) {
ans += dfs(root.right, low, high);
}
return ans;
}
}