2251. Number of Flowers in Full Bloom
Description
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array flowers, where flowers[i] = [starti, endi] means the ith flower will be in full bloom from starti to endi (inclusive). You are also given a 0-indexed integer array people of size n, where people[i] is the time that the ith person will arrive to see the flowers.
Return an integer array answer of size n, where answer[i] is the number of flowers that are in full bloom when the ith person arrives.
Example 1:
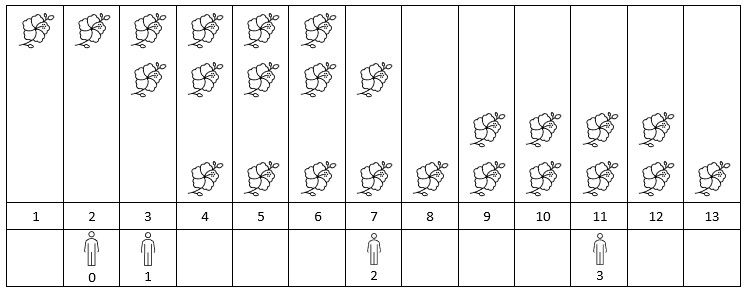
Input: flowers = [[1,6],[3,7],[9,12],[4,13]], people = [2,3,7,11] Output: [1,2,2,2] Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival.
Example 2:
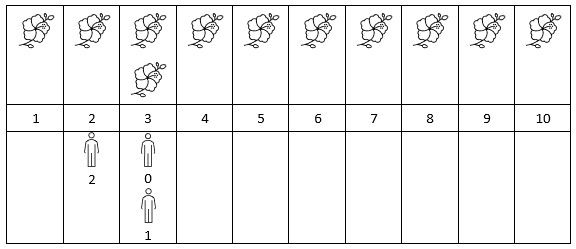
Input: flowers = [[1,10],[3,3]], people = [3,3,2] Output: [2,2,1] Explanation: The figure above shows the times when the flowers are in full bloom and when the people arrive. For each person, we return the number of flowers in full bloom during their arrival.
Constraints:
1 <= flowers.length <= 5 * 104flowers[i].length == 21 <= starti <= endi <= 1091 <= people.length <= 5 * 1041 <= people[i] <= 109
Solutions
Solution 1: Sorting + Binary Search
We sort the flowers by their start and end times. Then, for each person, we can use binary search to find the number of flowers in bloom when they arrive. This means finding the number of flowers that have started blooming by the time each person arrives, minus the number of flowers that have wilted by that time, to get the answer.
The time complexity is $O((m + n) \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Here, $n$ and $m$ are the lengths of the arrays $\textit{flowers}$ and $\textit{people}$, respectively.
Python3
class Solution:
def fullBloomFlowers(
self, flowers: List[List[int]], people: List[int]
) -> List[int]:
start, end = sorted(a for a, _ in flowers), sorted(b for _, b in flowers)
return [bisect_right(start, p) - bisect_left(end, p) for p in people]
Java
class Solution {
public int[] fullBloomFlowers(int[][] flowers, int[] people) {
int n = flowers.length;
int[] start = new int[n];
int[] end = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
start[i] = flowers[i][0];
end[i] = flowers[i][1];
}
Arrays.sort(start);
Arrays.sort(end);
int m = people.length;
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
ans[i] = search(start, people[i] + 1) - search(end, people[i]);
}
return ans;
}
private int search(int[] nums, int x) {
int l = 0, r = nums.length;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (nums[mid] >= x) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> fullBloomFlowers(vector<vector<int>>& flowers, vector<int>& people) {
int n = flowers.size();
vector<int> start;
vector<int> end;
for (auto& f : flowers) {
start.push_back(f[0]);
end.push_back(f[1]);
}
sort(start.begin(), start.end());
sort(end.begin(), end.end());
vector<int> ans;
for (auto& p : people) {
auto r = upper_bound(start.begin(), start.end(), p) - start.begin();
auto l = lower_bound(end.begin(), end.end(), p) - end.begin();
ans.push_back(r - l);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func fullBloomFlowers(flowers [][]int, people []int) (ans []int) {
n := len(flowers)
start := make([]int, n)
end := make([]int, n)
for i, f := range flowers {
start[i] = f[0]
end[i] = f[1]
}
sort.Ints(start)
sort.Ints(end)
for _, p := range people {
r := sort.SearchInts(start, p+1)
l := sort.SearchInts(end, p)
ans = append(ans, r-l)
}
return
}
TypeScript
function fullBloomFlowers(flowers: number[][], people: number[]): number[] {
const n = flowers.length;
const start = new Array(n).fill(0);
const end = new Array(n).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
start[i] = flowers[i][0];
end[i] = flowers[i][1];
}
start.sort((a, b) => a - b);
end.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const ans: number[] = [];
for (const p of people) {
const r = search(start, p + 1);
const l = search(end, p);
ans.push(r - l);
}
return ans;
}
function search(nums: number[], x: number): number {
let l = 0;
let r = nums.length;
while (l < r) {
const mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (nums[mid] >= x) {
r = mid;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return l;
}
Rust
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
impl Solution {
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn full_bloom_flowers(flowers: Vec<Vec<i32>>, people: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = people.len();
// First sort the people vector based on the first item
let mut people: Vec<(usize, i32)> = people.into_iter().enumerate().map(|x| x).collect();
people.sort_by(|lhs, rhs| lhs.1.cmp(&rhs.1));
// Initialize the difference vector
let mut diff = BTreeMap::new();
let mut ret = vec![0; n];
for f in flowers {
let (left, right) = (f[0], f[1]);
diff.entry(left)
.and_modify(|x| {
*x += 1;
})
.or_insert(1);
diff.entry(right + 1)
.and_modify(|x| {
*x -= 1;
})
.or_insert(-1);
}
let mut sum = 0;
let mut i = 0;
for (k, v) in diff {
while i < n && people[i].1 < k {
ret[people[i].0] += sum;
i += 1;
}
sum += v;
}
ret
}
}
Solution 2: Difference Array + Sorting + Offline Query
We can use a difference array to maintain the number of flowers at each time point. Next, we sort $people$ by their arrival times in ascending order. When each person arrives, we perform a prefix sum operation on the difference array to get the answer.
The time complexity is $O(m \times \log m + n \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n + m)$. Here, $n$ and $m$ are the lengths of the arrays $\textit{flowers}$ and $\textit{people}$, respectively.
Python3
class Solution:
def fullBloomFlowers(
self, flowers: List[List[int]], people: List[int]
) -> List[int]:
d = defaultdict(int)
for st, ed in flowers:
d[st] += 1
d[ed + 1] -= 1
ts = sorted(d)
s = i = 0
m = len(people)
ans = [0] * m
for t, j in sorted(zip(people, range(m))):
while i < len(ts) and ts[i] <= t:
s += d[ts[i]]
i += 1
ans[j] = s
return ans
Java
class Solution {
public int[] fullBloomFlowers(int[][] flowers, int[] people) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> d = new TreeMap<>();
for (int[] f : flowers) {
d.merge(f[0], 1, Integer::sum);
d.merge(f[1] + 1, -1, Integer::sum);
}
int s = 0;
int m = people.length;
Integer[] idx = new Integer[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
idx[i] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(idx, Comparator.comparingInt(i -> people[i]));
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int i : idx) {
int t = people[i];
while (!d.isEmpty() && d.firstKey() <= t) {
s += d.pollFirstEntry().getValue();
}
ans[i] = s;
}
return ans;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> fullBloomFlowers(vector<vector<int>>& flowers, vector<int>& people) {
map<int, int> d;
for (auto& f : flowers) {
d[f[0]]++;
d[f[1] + 1]--;
}
int m = people.size();
vector<int> idx(m);
iota(idx.begin(), idx.end(), 0);
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(), [&](int i, int j) {
return people[i] < people[j];
});
vector<int> ans(m);
int s = 0;
for (int i : idx) {
int t = people[i];
while (!d.empty() && d.begin()->first <= t) {
s += d.begin()->second;
d.erase(d.begin());
}
ans[i] = s;
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func fullBloomFlowers(flowers [][]int, people []int) []int {
d := map[int]int{}
for _, f := range flowers {
d[f[0]]++
d[f[1]+1]--
}
ts := []int{}
for t := range d {
ts = append(ts, t)
}
sort.Ints(ts)
m := len(people)
idx := make([]int, m)
for i := range idx {
idx[i] = i
}
sort.Slice(idx, func(i, j int) bool { return people[idx[i]] < people[idx[j]] })
ans := make([]int, m)
s, i := 0, 0
for _, j := range idx {
t := people[j]
for i < len(ts) && ts[i] <= t {
s += d[ts[i]]
i++
}
ans[j] = s
}
return ans
}
TypeScript
function fullBloomFlowers(flowers: number[][], people: number[]): number[] {
const d: Map<number, number> = new Map();
for (const [st, ed] of flowers) {
d.set(st, (d.get(st) || 0) + 1);
d.set(ed + 1, (d.get(ed + 1) || 0) - 1);
}
const ts = [...d.keys()].sort((a, b) => a - b);
let s = 0;
let i = 0;
const m = people.length;
const idx: number[] = [...Array(m)].map((_, i) => i).sort((a, b) => people[a] - people[b]);
const ans = Array(m).fill(0);
for (const j of idx) {
const t = people[j];
while (i < ts.length && ts[i] <= t) {
s += d.get(ts[i])!;
++i;
}
ans[j] = s;
}
return ans;
}