328. 奇偶链表
题目描述
给定单链表的头节点 head ,将所有索引为奇数的节点和索引为偶数的节点分别组合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。
第一个节点的索引被认为是 奇数 , 第二个节点的索引为 偶数 ,以此类推。
请注意,偶数组和奇数组内部的相对顺序应该与输入时保持一致。
你必须在 O(1) 的额外空间复杂度和 O(n) 的时间复杂度下解决这个问题。
示例 1:
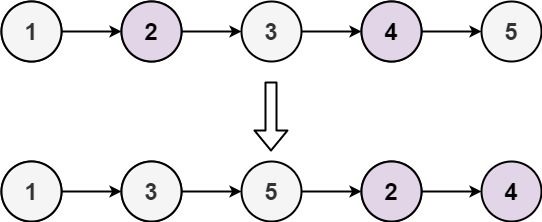
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出: [1,3,5,2,4]
示例 2:
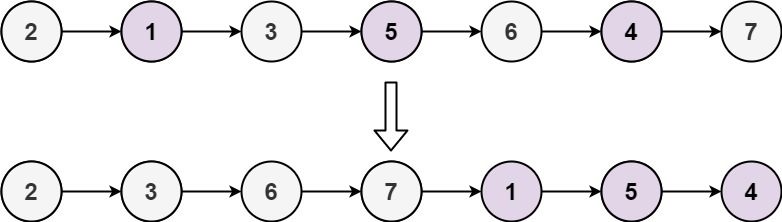
输入: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7] 输出: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]
提示:
n ==链表中的节点数0 <= n <= 104-106 <= Node.val <= 106
解法
方法一:一次遍历
我们可以用两个指针 $a$ 和 $b$ 分别表示奇数节点和偶数节点的尾节点。初始时,指针 $a$ 指向链表的头节点 $head$,指针 $b$ 指向链表的第二个节点 $head.next$。另外,我们用一个指针 $c$ 指向偶数节点的头节点 $head.next$,即指针 $b$ 的初始位置。
遍历链表,我们将指针 $a$ 指向 $b$ 的下一个节点,即 $a.next = b.next$,然后将指针 $a$ 向后移动一位,即 $a = a.next$;将指针 $b$ 指向 $a$ 的下一个节点,即 $b.next = a.next$,然后将指针 $b$ 向后移动一位,即 $b = b.next$。继续遍历,直到 $b$ 到达链表的末尾。
最后,我们将奇数节点的尾节点 $a$ 指向偶数节点的头节点 $c$,即 $a.next = c$,然后返回链表的头节点 $head$ 即可。
时间复杂度 $O(n)$,其中 $n$ 是链表的长度,需要遍历链表一次。空间复杂度 $O(1)$。只需要维护有限的指针。
Python3
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if head is None:
return None
a = head
b = c = head.next
while b and b.next:
a.next = b.next
a = a.next
b.next = a.next
b = b.next
a.next = c
return head
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode a = head;
ListNode b = head.next, c = b;
while (b != null && b.next != null) {
a.next = b.next;
a = a.next;
b.next = a.next;
b = b.next;
}
a.next = c;
return head;
}
}
C++
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) {
return nullptr;
}
ListNode* a = head;
ListNode *b = head->next, *c = b;
while (b && b->next) {
a->next = b->next;
a = a->next;
b->next = a->next;
b = b->next;
}
a->next = c;
return head;
}
};
Go
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* type ListNode struct {
* Val int
* Next *ListNode
* }
*/
func oddEvenList(head *ListNode) *ListNode {
if head == nil {
return nil
}
a := head
b, c := head.Next, head.Next
for b != nil && b.Next != nil {
a.Next = b.Next
a = a.Next
b.Next = a.Next
b = b.Next
}
a.Next = c
return head
}
TypeScript
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function oddEvenList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
if (!head) {
return null;
}
let [a, b, c] = [head, head.next, head.next];
while (b && b.next) {
a.next = b.next;
a = a.next;
b.next = a.next;
b = b.next;
}
a.next = c;
return head;
}