11. Container With Most Water
Description
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
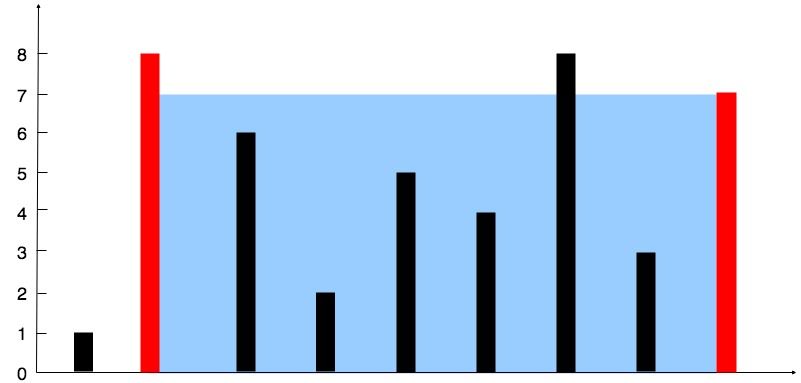
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49 Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1] Output: 1
Constraints:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= height[i] <= 104
Solutions
Solution 1: Two Pointers
We use two pointers $l$ and $r$ to point to the left and right ends of the array, respectively, i.e., $l = 0$ and $r = n - 1$, where $n$ is the length of the array.
Next, we use a variable $\textit{ans}$ to record the maximum capacity of the container, initially set to $0$.
Then, we start a loop. In each iteration, we calculate the current capacity of the container, i.e., $\textit{min}(height[l], height[r]) \times (r - l)$, and compare it with $\textit{ans}$, assigning the larger value to $\textit{ans}$. Then, we compare the values of $height[l]$ and $height[r]$. If $\textit{height}[l] < \textit{height}[r]$, moving the $r$ pointer will not improve the result because the height of the container is determined by the shorter vertical line, so we move the $l$ pointer. Otherwise, we move the $r$ pointer.
After the iteration, we return $\textit{ans}$.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array $\textit{height}$. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
Python3
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
l, r = 0, len(height) - 1
ans = 0
while l < r:
t = min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l)
ans = max(ans, t)
if height[l] < height[r]:
l += 1
else:
r -= 1
return ans
Java
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int l = 0, r = height.length - 1;
int ans = 0;
while (l < r) {
int t = Math.min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
ans = Math.max(ans, t);
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
++l;
} else {
--r;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxArea(vector<int>& height) {
int l = 0, r = height.size() - 1;
int ans = 0;
while (l < r) {
int t = min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
ans = max(ans, t);
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
++l;
} else {
--r;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maxArea(height []int) (ans int) {
l, r := 0, len(height)-1
for l < r {
t := min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l)
ans = max(ans, t)
if height[l] < height[r] {
l++
} else {
r--
}
}
return
}
TypeScript
function maxArea(height: number[]): number {
let [l, r] = [0, height.length - 1];
let ans = 0;
while (l < r) {
const t = Math.min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
ans = Math.max(ans, t);
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
++l;
} else {
--r;
}
}
return ans;
}
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn max_area(height: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut l = 0;
let mut r = height.len() - 1;
let mut ans = 0;
while l < r {
ans = ans.max(height[l].min(height[r]) * ((r - l) as i32));
if height[l] < height[r] {
l += 1;
} else {
r -= 1;
}
}
ans
}
}
JavaScript
/**
* @param {number[]} height
* @return {number}
*/
var maxArea = function (height) {
let [l, r] = [0, height.length - 1];
let ans = 0;
while (l < r) {
const t = Math.min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
ans = Math.max(ans, t);
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
++l;
} else {
--r;
}
}
return ans;
};
C#
public class Solution {
public int MaxArea(int[] height) {
int l = 0, r = height.Length - 1;
int ans = 0;
while (l < r) {
int t = Math.Min(height[l], height[r]) * (r - l);
ans = Math.Max(ans, t);
if (height[l] < height[r]) {
++l;
} else {
--r;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
PHP
class Solution {
/**
* @param Integer[] $height
* @return Integer
*/
function maxArea($height) {
$l = 0;
$r = count($height) - 1;
$ans = 0;
while ($l < $r) {
$t = min($height[$l], $height[$r]) * ($r - $l);
$ans = max($ans, $t);
if ($height[$l] < $height[$r]) {
++$l;
} else {
--$r;
}
}
return $ans;
}
}