1401. Circle and Rectangle Overlapping
Description
You are given a circle represented as (radius, xCenter, yCenter) and an axis-aligned rectangle represented as (x1, y1, x2, y2), where (x1, y1) are the coordinates of the bottom-left corner, and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of the top-right corner of the rectangle.
Return true if the circle and rectangle are overlapped otherwise return false. In other words, check if there is any point (xi, yi) that belongs to the circle and the rectangle at the same time.
Example 1:
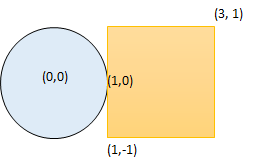
Input: radius = 1, xCenter = 0, yCenter = 0, x1 = 1, y1 = -1, x2 = 3, y2 = 1 Output: true Explanation: Circle and rectangle share the point (1,0).
Example 2:
Input: radius = 1, xCenter = 1, yCenter = 1, x1 = 1, y1 = -3, x2 = 2, y2 = -1 Output: false
Example 3:
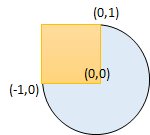
Input: radius = 1, xCenter = 0, yCenter = 0, x1 = -1, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 1 Output: true
Constraints:
1 <= radius <= 2000-104 <= xCenter, yCenter <= 104-104 <= x1 < x2 <= 104-104 <= y1 < y2 <= 104
Solutions
Solution 1: Mathematics
For a point $(x, y)$, its shortest distance to the center of the circle $(xCenter, yCenter)$ is $\sqrt{(x - xCenter)^2 + (y - yCenter)^2}$. If this distance is less than or equal to the radius $radius$, then this point is within the circle (including the boundary).
For points within the rectangle (including the boundary), their x-coordinates $x$ satisfy $x_1 \leq x \leq x_2$, and their y-coordinates $y$ satisfy $y_1 \leq y \leq y_2$. To determine whether the circle and rectangle overlap, we need to find a point $(x, y)$ within the rectangle such that $a = |x - xCenter|$ and $b = |y - yCenter|$ are minimized. If $a^2 + b^2 \leq radius^2$, then the circle and rectangle overlap.
Therefore, the problem is transformed into finding the minimum value of $a = |x - xCenter|$ when $x \in [x_1, x_2]$, and the minimum value of $b = |y - yCenter|$ when $y \in [y_1, y_2]$.
For $x \in [x_1, x_2]$:
If $x_1 \leq xCenter \leq x_2$, then the minimum value of $|x - xCenter|$ is $0$;
If $xCenter < x_1$, then the minimum value of $|x - xCenter|$ is $x_1 - xCenter$;
If $xCenter > x_2$, then the minimum value of $|x - xCenter|$ is $xCenter - x_2$.
Similarly, we can find the minimum value of $|y - yCenter|$ when $y \in [y_1, y_2]$. We can use a function $f(i, j, k)$ to handle the above situations.
That is, $a = f(x_1, x_2, xCenter)$, $b = f(y_1, y_2, yCenter)$. If $a^2 + b^2 \leq radius^2$, then the circle and rectangle overlap.
Python3
class Solution:
def checkOverlap(
self,
radius: int,
xCenter: int,
yCenter: int,
x1: int,
y1: int,
x2: int,
y2: int,
) -> bool:
def f(i: int, j: int, k: int) -> int:
if i <= k <= j:
return 0
return i - k if k < i else k - j
a = f(x1, x2, xCenter)
b = f(y1, y2, yCenter)
return a * a + b * b <= radius * radius
Java
class Solution {
public boolean checkOverlap(
int radius, int xCenter, int yCenter, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
int a = f(x1, x2, xCenter);
int b = f(y1, y2, yCenter);
return a * a + b * b <= radius * radius;
}
private int f(int i, int j, int k) {
if (i <= k && k <= j) {
return 0;
}
return k < i ? i - k : k - j;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool checkOverlap(int radius, int xCenter, int yCenter, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {
auto f = [](int i, int j, int k) -> int {
if (i <= k && k <= j) {
return 0;
}
return k < i ? i - k : k - j;
};
int a = f(x1, x2, xCenter);
int b = f(y1, y2, yCenter);
return a * a + b * b <= radius * radius;
}
};
Go
func checkOverlap(radius int, xCenter int, yCenter int, x1 int, y1 int, x2 int, y2 int) bool {
f := func(i, j, k int) int {
if i <= k && k <= j {
return 0
}
if k < i {
return i - k
}
return k - j
}
a := f(x1, x2, xCenter)
b := f(y1, y2, yCenter)
return a*a+b*b <= radius*radius
}
TypeScript
function checkOverlap(
radius: number,
xCenter: number,
yCenter: number,
x1: number,
y1: number,
x2: number,
y2: number,
): boolean {
const f = (i: number, j: number, k: number) => {
if (i <= k && k <= j) {
return 0;
}
return k < i ? i - k : k - j;
};
const a = f(x1, x2, xCenter);
const b = f(y1, y2, yCenter);
return a * a + b * b <= radius * radius;
}