559. Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
Description
Given a n-ary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal, each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples).
Example 1:
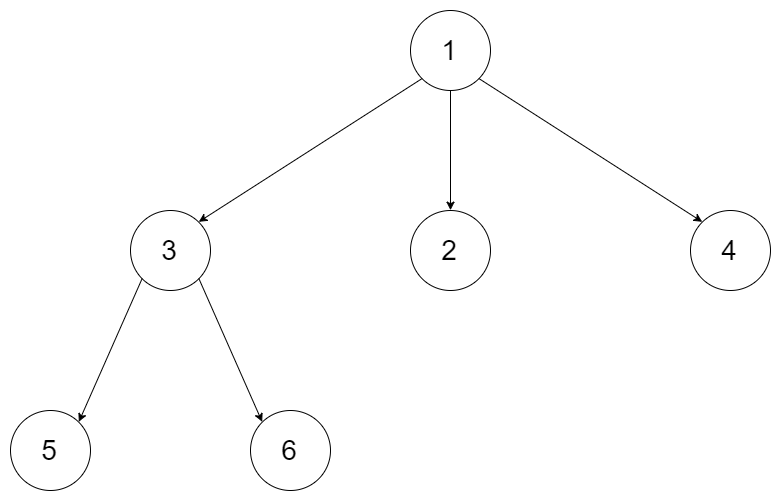
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: 3
Example 2:
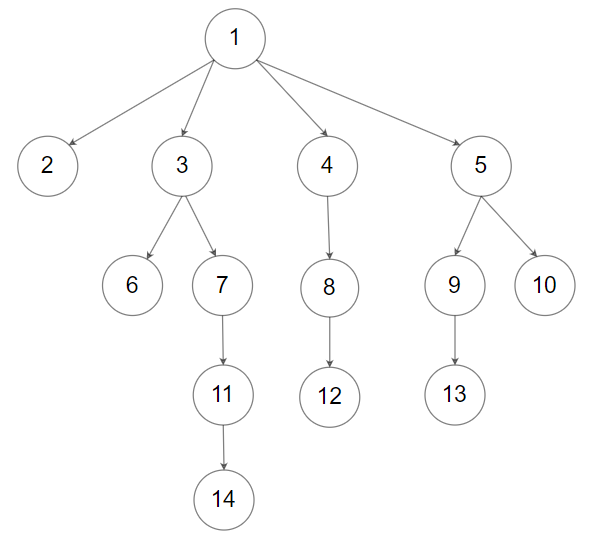
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: 5
Constraints:
- The total number of nodes is in the range
[0, 104]. - The depth of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to
1000.
Solutions
Solution 1: Recursion
First, we check if $\textit{root}$ is null. If it is, we return 0. Otherwise, we initialize a variable $\textit{mx}$ to record the maximum depth of the child nodes, then traverse all the child nodes of $\textit{root}$, recursively call the $\text{maxDepth}$ function, and update the value of $\textit{mx}$. Finally, we return $\textit{mx} + 1$.
The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the number of nodes.
Python3
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:
def __init__(self, val: Optional[int] = None, children: Optional[List['Node']] = None):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: "Node") -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
mx = 0
for child in root.children:
mx = max(mx, self.maxDepth(child))
return 1 + mx
Java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int mx = 0;
for (Node child : root.children) {
mx = Math.max(mx, maxDepth(child));
}
return 1 + mx;
}
}
C++
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
vector<Node*> children;
Node() {}
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
Node(int _val, vector<Node*> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(Node* root) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
int mx = 0;
for (Node* child : root->children) {
mx = max(mx, maxDepth(child));
}
return mx + 1;
}
};
Go
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* type Node struct {
* Val int
* Children []*Node
* }
*/
func maxDepth(root *Node) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
mx := 0
for _, child := range root.Children {
mx = max(mx, maxDepth(child))
}
return 1 + mx
}
TypeScript
/**
* Definition for _Node.
* class _Node {
* val: number
* children: _Node[]
*
* constructor(val?: number, children?: _Node[]) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.children = (children===undefined ? [] : children)
* }
* }
*/
function maxDepth(root: _Node | null): number {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
return 1 + Math.max(...root.children.map(child => maxDepth(child)), 0);
}