1478. Allocate Mailboxes
Description
Given the array houses where houses[i] is the location of the ith house along a street and an integer k, allocate k mailboxes in the street.
Return the minimum total distance between each house and its nearest mailbox.
The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bit integer.
Example 1:
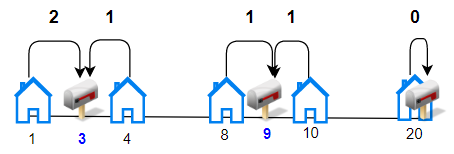
Input: houses = [1,4,8,10,20], k = 3 Output: 5 Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3, 9 and 20. Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |3-1| + |4-3| + |9-8| + |10-9| + |20-20| = 5
Example 2:
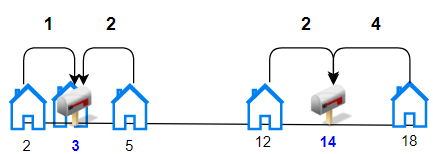
Input: houses = [2,3,5,12,18], k = 2 Output: 9 Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3 and 14. Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |2-3| + |3-3| + |5-3| + |12-14| + |18-14| = 9.
Constraints:
1 <= k <= houses.length <= 1001 <= houses[i] <= 104- All the integers of
housesare unique.
Solutions
Solution 1: Dynamic Programming
We define $f[i][j]$ to represent the minimum total distance between the houses and their nearest mailbox, when placing $j$ mailboxes among the first $i+1$ houses. Initially, $f[i][j] = \infty$, and the final answer will be $f[n-1][k]$.
We can iterate over the last house $p$ controlled by the $j-1$-th mailbox, i.e., $0 \leq p \leq i-1$. The $j$-th mailbox will control the houses in the range $[p+1, \dots, i]$. Let $g[i][j]$ denote the minimum total distance when placing a mailbox for the houses in the range $[i, \dots, j]$. The state transition equation is:
$$ f[i][j] = \min_{0 \leq p \leq i-1} {f[p][j-1] + g[p+1][i]} $$
where $g[i][j]$ is computed as follows:
$$ g[i][j] = g[i + 1][j - 1] + \textit{houses}[j] - \textit{houses}[i] $$
The time complexity is $O(n^2 \times k)$, and the space complexity is $O(n^2)$, where $n$ is the number of houses.
Python3
class Solution:
def minDistance(self, houses: List[int], k: int) -> int:
houses.sort()
n = len(houses)
g = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n - 2, -1, -1):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
g[i][j] = g[i + 1][j - 1] + houses[j] - houses[i]
f = [[inf] * (k + 1) for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
f[i][1] = g[0][i]
for j in range(2, min(k + 1, i + 2)):
for p in range(i):
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[p][j - 1] + g[p + 1][i])
return f[-1][k]
Java
class Solution {
public int minDistance(int[] houses, int k) {
Arrays.sort(houses);
int n = houses.length;
int[][] g = new int[n][n];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = g[i + 1][j - 1] + houses[j] - houses[i];
}
}
int[][] f = new int[n][k + 1];
final int inf = 1 << 30;
for (int[] e : f) {
Arrays.fill(e, inf);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
f[i][1] = g[0][i];
for (int j = 2; j <= k && j <= i + 1; ++j) {
for (int p = 0; p < i; ++p) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[p][j - 1] + g[p + 1][i]);
}
}
}
return f[n - 1][k];
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(vector<int>& houses, int k) {
int n = houses.size();
sort(houses.begin(), houses.end());
int g[n][n];
memset(g, 0, sizeof(g));
for (int i = n - 2; ~i; --i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
g[i][j] = g[i + 1][j - 1] + houses[j] - houses[i];
}
}
int f[n][k + 1];
memset(f, 0x3f, sizeof(f));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
f[i][1] = g[0][i];
for (int j = 1; j <= k && j <= i + 1; ++j) {
for (int p = 0; p < i; ++p) {
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[p][j - 1] + g[p + 1][i]);
}
}
}
return f[n - 1][k];
}
};
Go
func minDistance(houses []int, k int) int {
sort.Ints(houses)
n := len(houses)
g := make([][]int, n)
f := make([][]int, n)
const inf = 1 << 30
for i := range g {
g[i] = make([]int, n)
f[i] = make([]int, k+1)
for j := range f[i] {
f[i][j] = inf
}
}
for i := n - 2; i >= 0; i-- {
for j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {
g[i][j] = g[i+1][j-1] + houses[j] - houses[i]
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
f[i][1] = g[0][i]
for j := 2; j <= k && j <= i+1; j++ {
for p := 0; p < i; p++ {
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j], f[p][j-1]+g[p+1][i])
}
}
}
return f[n-1][k]
}
TypeScript
function minDistance(houses: number[], k: number): number {
houses.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const n = houses.length;
const g: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(n).fill(0));
for (let i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
for (let j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
g[i][j] = g[i + 1][j - 1] + houses[j] - houses[i];
}
}
const inf = Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
const f: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(k + 1).fill(inf));
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
f[i][1] = g[0][i];
}
for (let j = 2; j <= k; j++) {
for (let i = j - 1; i < n; i++) {
for (let p = i - 1; p >= 0; p--) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[p][j - 1] + g[p + 1][i]);
}
}
}
return f[n - 1][k];
}