3531. 统计被覆盖的建筑
题目描述
给你一个正整数 n,表示一个 n x n 的城市,同时给定一个二维数组 buildings,其中 buildings[i] = [x, y] 表示位于坐标 [x, y] 的一个 唯一 建筑。
如果一个建筑在四个方向(左、右、上、下)中每个方向上都至少存在一个建筑,则称该建筑 被覆盖 。
返回 被覆盖 的建筑数量。
示例 1:
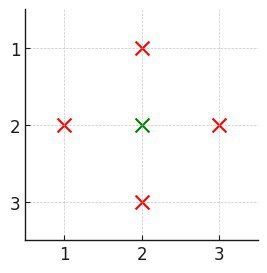
输入: n = 3, buildings = [[1,2],[2,2],[3,2],[2,1],[2,3]]
输出: 1
解释:
- 只有建筑
[2,2]被覆盖,因为它在每个方向上都至少存在一个建筑:<ul> <li>上方 (<code>[1,2]</code>)</li> <li>下方 (<code>[3,2]</code>)</li> <li>左方 (<code>[2,1]</code>)</li> <li>右方 (<code>[2,3]</code>)</li> </ul> </li> <li>因此,被覆盖的建筑数量是 1。</li>
示例 2:
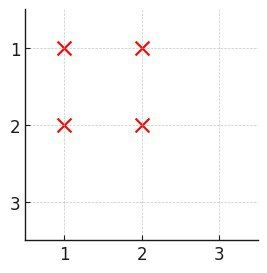
输入: n = 3, buildings = [[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[2,2]]
输出: 0
解释:
- 没有任何一个建筑在每个方向上都有至少一个建筑。
示例 3:
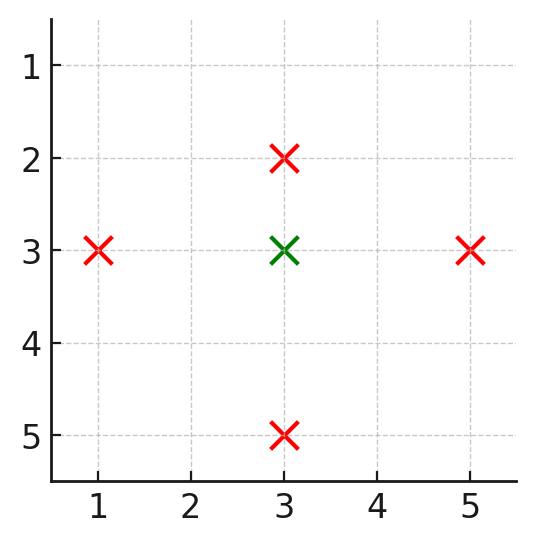
输入: n = 5, buildings = [[1,3],[3,2],[3,3],[3,5],[5,3]]
输出: 1
解释:
- 只有建筑
[3,3]被覆盖,因为它在每个方向上至少存在一个建筑:<ul> <li>上方 (<code>[1,3]</code>)</li> <li>下方 (<code>[5,3]</code>)</li> <li>左方 (<code>[3,2]</code>)</li> <li>右方 (<code>[3,5]</code>)</li> </ul> </li> <li>因此,被覆盖的建筑数量是 1。</li>
提示:
2 <= n <= 1051 <= buildings.length <= 105buildings[i] = [x, y]1 <= x, y <= nbuildings中所有坐标均 唯一 。
解法
方法一:哈希表 + 排序
我们可以将建筑按照横坐标和纵坐标进行分组,分别记录在哈希表 $\text{g1}$ 和 $\text{g2}$ 中,其中 $\text{g1[x]}$ 表示所有横坐标为 $x$ 的纵坐标,而 $\text{g2[y]}$ 表示所有纵坐标为 $y$ 的横坐标,然后我们将其进行排序。
接下来,我们遍历所有建筑,对于当前建筑 $(x, y)$,我们通过哈希表获取对应的纵坐标列表 $l_1$ 和横坐标列表 $l_2$,并检查条件以确定建筑是否被覆盖。覆盖的条件是 $l_2[0] < x < l_2[-1]$ 且 $l_1[0] < y < l_1[-1]$,若是,我们将答案加一。
遍历结束后,返回答案即可。
时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是建筑物的数量。
Python3
class Solution:
def countCoveredBuildings(self, n: int, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> int:
g1 = defaultdict(list)
g2 = defaultdict(list)
for x, y in buildings:
g1[x].append(y)
g2[y].append(x)
for x in g1:
g1[x].sort()
for y in g2:
g2[y].sort()
ans = 0
for x, y in buildings:
l1 = g1[x]
l2 = g2[y]
if l2[0] < x < l2[-1] and l1[0] < y < l1[-1]:
ans += 1
return ans
Java
class Solution {
public int countCoveredBuildings(int n, int[][] buildings) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> g2 = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] building : buildings) {
int x = building[0], y = building[1];
g1.computeIfAbsent(x, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(y);
g2.computeIfAbsent(y, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(x);
}
for (var e : g1.entrySet()) {
Collections.sort(e.getValue());
}
for (var e : g2.entrySet()) {
Collections.sort(e.getValue());
}
int ans = 0;
for (int[] building : buildings) {
int x = building[0], y = building[1];
List<Integer> l1 = g1.get(x);
List<Integer> l2 = g2.get(y);
if (l2.get(0) < x && x < l2.get(l2.size() - 1) && l1.get(0) < y
&& y < l1.get(l1.size() - 1)) {
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
int countCoveredBuildings(int n, vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> g1;
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> g2;
for (const auto& building : buildings) {
int x = building[0], y = building[1];
g1[x].push_back(y);
g2[y].push_back(x);
}
for (auto& e : g1) {
sort(e.second.begin(), e.second.end());
}
for (auto& e : g2) {
sort(e.second.begin(), e.second.end());
}
int ans = 0;
for (const auto& building : buildings) {
int x = building[0], y = building[1];
const vector<int>& l1 = g1[x];
const vector<int>& l2 = g2[y];
if (l2[0] < x && x < l2[l2.size() - 1] && l1[0] < y && y < l1[l1.size() - 1]) {
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func countCoveredBuildings(n int, buildings [][]int) (ans int) {
g1 := make(map[int][]int)
g2 := make(map[int][]int)
for _, building := range buildings {
x, y := building[0], building[1]
g1[x] = append(g1[x], y)
g2[y] = append(g2[y], x)
}
for _, list := range g1 {
sort.Ints(list)
}
for _, list := range g2 {
sort.Ints(list)
}
for _, building := range buildings {
x, y := building[0], building[1]
l1 := g1[x]
l2 := g2[y]
if l2[0] < x && x < l2[len(l2)-1] && l1[0] < y && y < l1[len(l1)-1] {
ans++
}
}
return
}
TypeScript
function countCoveredBuildings(n: number, buildings: number[][]): number {
const g1: Map<number, number[]> = new Map();
const g2: Map<number, number[]> = new Map();
for (const [x, y] of buildings) {
if (!g1.has(x)) g1.set(x, []);
g1.get(x)?.push(y);
if (!g2.has(y)) g2.set(y, []);
g2.get(y)?.push(x);
}
for (const list of g1.values()) {
list.sort((a, b) => a - b);
}
for (const list of g2.values()) {
list.sort((a, b) => a - b);
}
let ans = 0;
for (const [x, y] of buildings) {
const l1 = g1.get(x)!;
const l2 = g2.get(y)!;
if (l2[0] < x && x < l2[l2.length - 1] && l1[0] < y && y < l1[l1.length - 1]) {
ans++;
}
}
return ans;
}