3148. Maximum Difference Score in a Grid
Description
You are given an m x n matrix grid consisting of positive integers. You can move from a cell in the matrix to any other cell that is either to the bottom or to the right (not necessarily adjacent). The score of a move from a cell with the value c1 to a cell with the value c2 is c2 - c1.
You can start at any cell, and you have to make at least one move.
Return the maximum total score you can achieve.
Example 1:
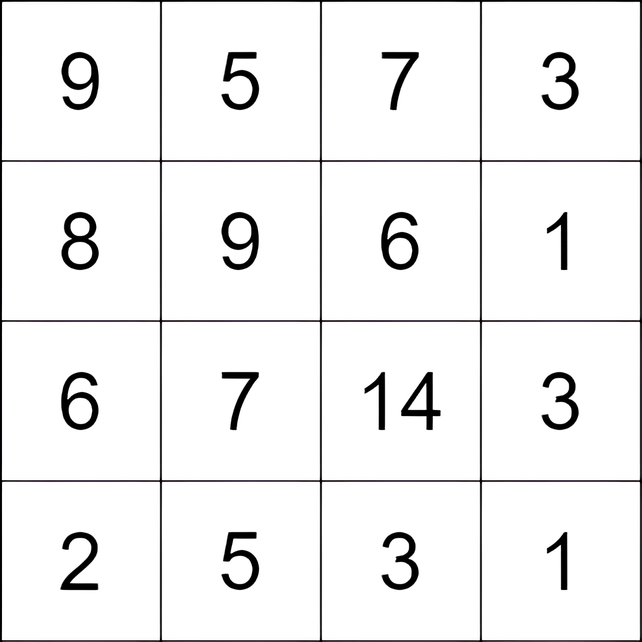
Input: grid = [[9,5,7,3],[8,9,6,1],[6,7,14,3],[2,5,3,1]]
Output: 9
Explanation: We start at the cell (0, 1), and we perform the following moves:
- Move from the cell (0, 1) to (2, 1) with a score of 7 - 5 = 2.
- Move from the cell (2, 1) to (2, 2) with a score of 14 - 7 = 7.
The total score is 2 + 7 = 9.
Example 2:
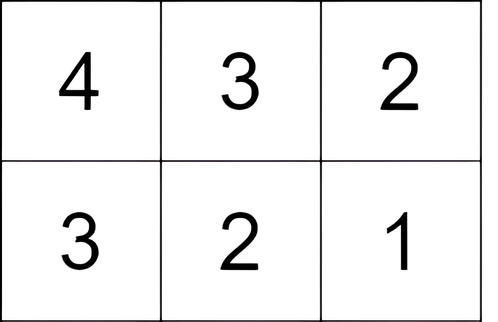
Input: grid = [[4,3,2],[3,2,1]]
Output: -1
Explanation: We start at the cell (0, 0), and we perform one move: (0, 0) to (0, 1). The score is 3 - 4 = -1.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 10004 <= m * n <= 1051 <= grid[i][j] <= 105
Solutions
Solution 1: Dynamic Programming
According to the problem description, if the values of the cells we pass through are $c_1, c_2, \cdots, c_k$, then our score is $c_2 - c_1 + c_3 - c_2 + \cdots + c_k - c_{k-1} = c_k - c_1$. Therefore, the problem is transformed into: for each cell $(i, j)$ of the matrix, if we take it as the endpoint, what is the minimum value of the starting point.
We can use dynamic programming to solve this problem. We define $f[i][j]$ as the minimum value of the path with $(i, j)$ as the endpoint. Then we can get the state transition equation:
$$ f[i][j] = \min(f[i-1][j], f[i][j-1], grid[i][j]) $$
So the answer is the maximum value of $\textit{grid}[i][j] - \min(f[i-1][j], f[i][j-1])$.
The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times n)$. Where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the matrix, respectively.
Python3
class Solution:
def maxScore(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
f = [[0] * len(grid[0]) for _ in range(len(grid))]
ans = -inf
for i, row in enumerate(grid):
for j, x in enumerate(row):
mi = inf
if i:
mi = min(mi, f[i - 1][j])
if j:
mi = min(mi, f[i][j - 1])
ans = max(ans, x - mi)
f[i][j] = min(x, mi)
return ans
Java
class Solution {
public int maxScore(List<List<Integer>> grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid.get(0).size();
final int inf = 1 << 30;
int ans = -inf;
int[][] f = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int mi = inf;
if (i > 0) {
mi = Math.min(mi, f[i - 1][j]);
}
if (j > 0) {
mi = Math.min(mi, f[i][j - 1]);
}
ans = Math.max(ans, grid.get(i).get(j) - mi);
f[i][j] = Math.min(grid.get(i).get(j), mi);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
int maxScore(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
const int inf = 1 << 30;
int ans = -inf;
int f[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
int mi = inf;
if (i) {
mi = min(mi, f[i - 1][j]);
}
if (j) {
mi = min(mi, f[i][j - 1]);
}
ans = max(ans, grid[i][j] - mi);
f[i][j] = min(grid[i][j], mi);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func maxScore(grid [][]int) int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
f := make([][]int, m)
for i := range f {
f[i] = make([]int, n)
}
const inf int = 1 << 30
ans := -inf
for i, row := range grid {
for j, x := range row {
mi := inf
if i > 0 {
mi = min(mi, f[i-1][j])
}
if j > 0 {
mi = min(mi, f[i][j-1])
}
ans = max(ans, x-mi)
f[i][j] = min(x, mi)
}
}
return ans
}
TypeScript
function maxScore(grid: number[][]): number {
const [m, n] = [grid.length, grid[0].length];
const f: number[][] = Array.from({ length: m }, () => Array.from({ length: n }, () => 0));
let ans = -Infinity;
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
let mi = Infinity;
if (i) {
mi = Math.min(mi, f[i - 1][j]);
}
if (j) {
mi = Math.min(mi, f[i][j - 1]);
}
ans = Math.max(ans, grid[i][j] - mi);
f[i][j] = Math.min(mi, grid[i][j]);
}
}
return ans;
}