3197. Find the Minimum Area to Cover All Ones II
Description
You are given a 2D binary array grid. You need to find 3 non-overlapping rectangles having non-zero areas with horizontal and vertical sides such that all the 1's in grid lie inside these rectangles.
Return the minimum possible sum of the area of these rectangles.
Note that the rectangles are allowed to touch.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: 5
Explanation:
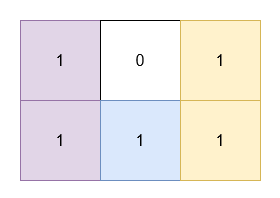
- The 1's at
(0, 0)and(1, 0)are covered by a rectangle of area 2. - The 1's at
(0, 2)and(1, 2)are covered by a rectangle of area 2. - The 1 at
(1, 1)is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,0,1,0],[0,1,0,1]]
Output: 5
Explanation:
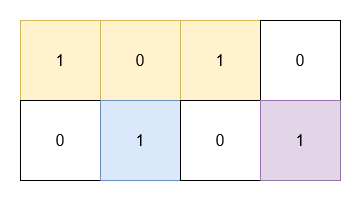
- The 1's at
(0, 0)and(0, 2)are covered by a rectangle of area 3. - The 1 at
(1, 1)is covered by a rectangle of area 1. - The 1 at
(1, 3)is covered by a rectangle of area 1.
Constraints:
1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 30grid[i][j]is either 0 or 1.- The input is generated such that there are at least three 1's in
grid.
Solutions
Solution 1: Enumeration
According to the problem description, we can use two dividing lines to split the rectangle into three parts. We calculate the minimum rectangular area containing all $1$s for each part and then take the minimum sum of the areas of the three parts.
We can enumerate the positions of the two dividing lines, which have $6$ possibilities:
Two horizontal splits
Two vertical splits
First perform a horizontal split, then a vertical split on the upper part
First perform a horizontal split, then a vertical split on the lower part
First perform a vertical split, then a horizontal split on the left part
First perform a vertical split, then a horizontal split on the right part
We can use a function $\textit{f}(i_1, j_1, i_2, j_2)$ to calculate the minimum rectangular area containing all $1$s from $(i_1, j_1)$ to $(i_2, j_2)$.
The time complexity is $O(m^2 \times n^2)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the rectangle, respectively. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
Python3
class Solution:
def minimumSum(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def f(i1: int, j1: int, i2: int, j2: int) -> int:
x1 = y1 = inf
x2 = y2 = -inf
for i in range(i1, i2 + 1):
for j in range(j1, j2 + 1):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
x1 = min(x1, i)
y1 = min(y1, j)
x2 = max(x2, i)
y2 = max(y2, j)
return (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
ans = m * n
for i1 in range(m - 1):
for i2 in range(i1 + 1, m - 1):
ans = min(
ans,
f(0, 0, i1, n - 1)
+ f(i1 + 1, 0, i2, n - 1)
+ f(i2 + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1),
)
for j1 in range(n - 1):
for j2 in range(j1 + 1, n - 1):
ans = min(
ans,
f(0, 0, m - 1, j1)
+ f(0, j1 + 1, m - 1, j2)
+ f(0, j2 + 1, m - 1, n - 1),
)
for i in range(m - 1):
for j in range(n - 1):
ans = min(
ans,
f(0, 0, i, j) + f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1),
)
ans = min(
ans,
f(0, 0, i, n - 1)
+ f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j)
+ f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1),
)
ans = min(
ans,
f(0, 0, i, j) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j) + f(0, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1),
)
ans = min(
ans,
f(0, 0, m - 1, j)
+ f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1)
+ f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1),
)
return ans
Java
class Solution {
private final int inf = 1 << 30;
private int[][] grid;
public int minimumSum(int[][] grid) {
this.grid = grid;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int ans = m * n;
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < m - 1; i1++) {
for (int i2 = i1 + 1; i2 < m - 1; i2++) {
ans = Math.min(
ans, f(0, 0, i1, n - 1) + f(i1 + 1, 0, i2, n - 1) + f(i2 + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1));
}
}
for (int j1 = 0; j1 < n - 1; j1++) {
for (int j2 = j1 + 1; j2 < n - 1; j2++) {
ans = Math.min(
ans, f(0, 0, m - 1, j1) + f(0, j1 + 1, m - 1, j2) + f(0, j2 + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
ans = Math.min(
ans, f(0, 0, i, j) + f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = Math.min(
ans, f(0, 0, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j) + f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = Math.min(
ans, f(0, 0, i, j) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j) + f(0, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = Math.min(
ans, f(0, 0, m - 1, j) + f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
}
}
return ans;
}
private int f(int i1, int j1, int i2, int j2) {
int x1 = inf, y1 = inf;
int x2 = -inf, y2 = -inf;
for (int i = i1; i <= i2; i++) {
for (int j = j1; j <= j2; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
x1 = Math.min(x1, i);
y1 = Math.min(y1, j);
x2 = Math.max(x2, i);
y2 = Math.max(y2, j);
}
}
}
return (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1);
}
}
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minimumSum(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size();
int n = grid[0].size();
int ans = m * n;
int inf = INT_MAX / 4;
auto f = [&](int i1, int j1, int i2, int j2) {
int x1 = inf, y1 = inf;
int x2 = -inf, y2 = -inf;
for (int i = i1; i <= i2; i++) {
for (int j = j1; j <= j2; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
x1 = min(x1, i);
y1 = min(y1, j);
x2 = max(x2, i);
y2 = max(y2, j);
}
}
}
return x1 > x2 || y1 > y2 ? inf : (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1);
};
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < m - 1; i1++) {
for (int i2 = i1 + 1; i2 < m - 1; i2++) {
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i1, n - 1) + f(i1 + 1, 0, i2, n - 1) + f(i2 + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1));
}
}
for (int j1 = 0; j1 < n - 1; j1++) {
for (int j2 = j1 + 1; j2 < n - 1; j2++) {
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, m - 1, j1) + f(0, j1 + 1, m - 1, j2) + f(0, j2 + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i, j) + f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j) + f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i, j) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j) + f(0, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, m - 1, j) + f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func minimumSum(grid [][]int) int {
m := len(grid)
n := len(grid[0])
ans := m * n
inf := math.MaxInt32
f := func(i1, j1, i2, j2 int) int {
x1, y1 := inf, inf
x2, y2 := -inf, -inf
for i := i1; i <= i2; i++ {
for j := j1; j <= j2; j++ {
if grid[i][j] == 1 {
x1 = min(x1, i)
y1 = min(y1, j)
x2 = max(x2, i)
y2 = max(y2, j)
}
}
}
if x1 == inf {
return 0
}
return (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
}
for i1 := 0; i1 < m-1; i1++ {
for i2 := i1 + 1; i2 < m-1; i2++ {
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i1, n-1)+f(i1+1, 0, i2, n-1)+f(i2+1, 0, m-1, n-1))
}
}
for j1 := 0; j1 < n-1; j1++ {
for j2 := j1 + 1; j2 < n-1; j2++ {
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, m-1, j1)+f(0, j1+1, m-1, j2)+f(0, j2+1, m-1, n-1))
}
}
for i := 0; i < m-1; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n-1; j++ {
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i, j)+f(0, j+1, i, n-1)+f(i+1, 0, m-1, n-1))
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i, n-1)+f(i+1, 0, m-1, j)+f(i+1, j+1, m-1, n-1))
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, i, j)+f(i+1, 0, m-1, j)+f(0, j+1, m-1, n-1))
ans = min(ans, f(0, 0, m-1, j)+f(0, j+1, i, n-1)+f(i+1, j+1, m-1, n-1))
}
}
return ans
}
TypeScript
function minimumSum(grid: number[][]): number {
const m = grid.length;
const n = grid[0].length;
let ans = m * n;
const inf = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
const f = (i1: number, j1: number, i2: number, j2: number): number => {
let [x1, y1] = [inf, inf];
let [x2, y2] = [-inf, -inf];
for (let i = i1; i <= i2; i++) {
for (let j = j1; j <= j2; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] === 1) {
x1 = Math.min(x1, i);
y1 = Math.min(y1, j);
x2 = Math.max(x2, i);
y2 = Math.max(y2, j);
}
}
}
return x1 === inf ? 0 : (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1);
};
for (let i1 = 0; i1 < m - 1; i1++) {
for (let i2 = i1 + 1; i2 < m - 1; i2++) {
ans = Math.min(
ans,
f(0, 0, i1, n - 1) + f(i1 + 1, 0, i2, n - 1) + f(i2 + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1),
);
}
}
for (let j1 = 0; j1 < n - 1; j1++) {
for (let j2 = j1 + 1; j2 < n - 1; j2++) {
ans = Math.min(
ans,
f(0, 0, m - 1, j1) + f(0, j1 + 1, m - 1, j2) + f(0, j2 + 1, m - 1, n - 1),
);
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n - 1; j++) {
ans = Math.min(ans, f(0, 0, i, j) + f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = Math.min(
ans,
f(0, 0, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j) + f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1),
);
ans = Math.min(ans, f(0, 0, i, j) + f(i + 1, 0, m - 1, j) + f(0, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1));
ans = Math.min(
ans,
f(0, 0, m - 1, j) + f(0, j + 1, i, n - 1) + f(i + 1, j + 1, m - 1, n - 1),
);
}
}
return ans;
}